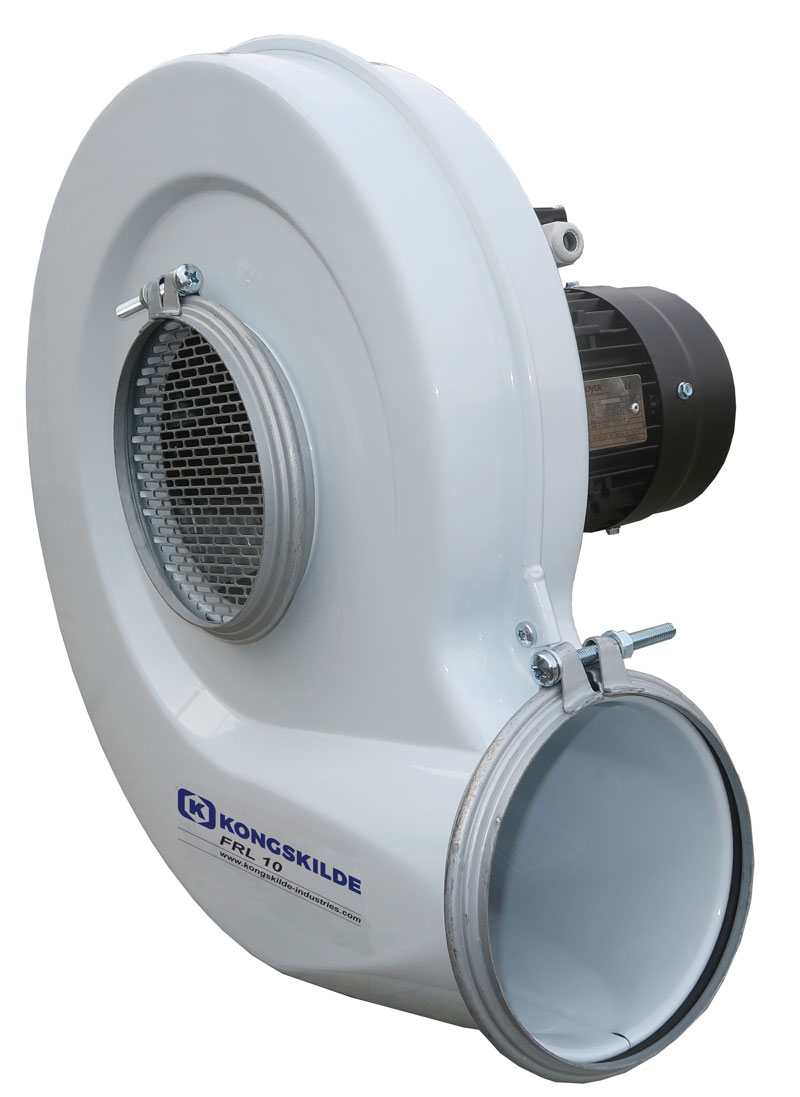
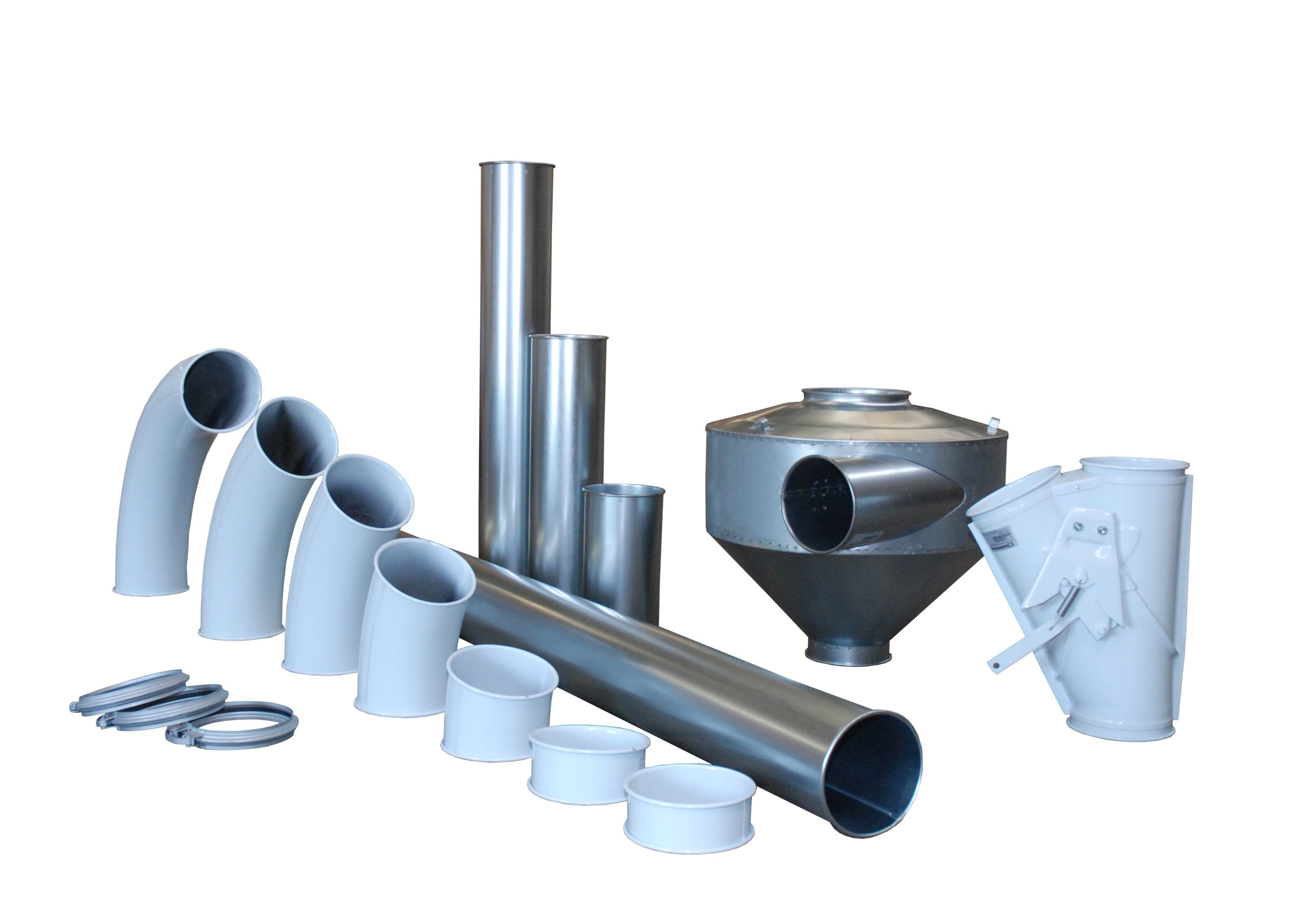
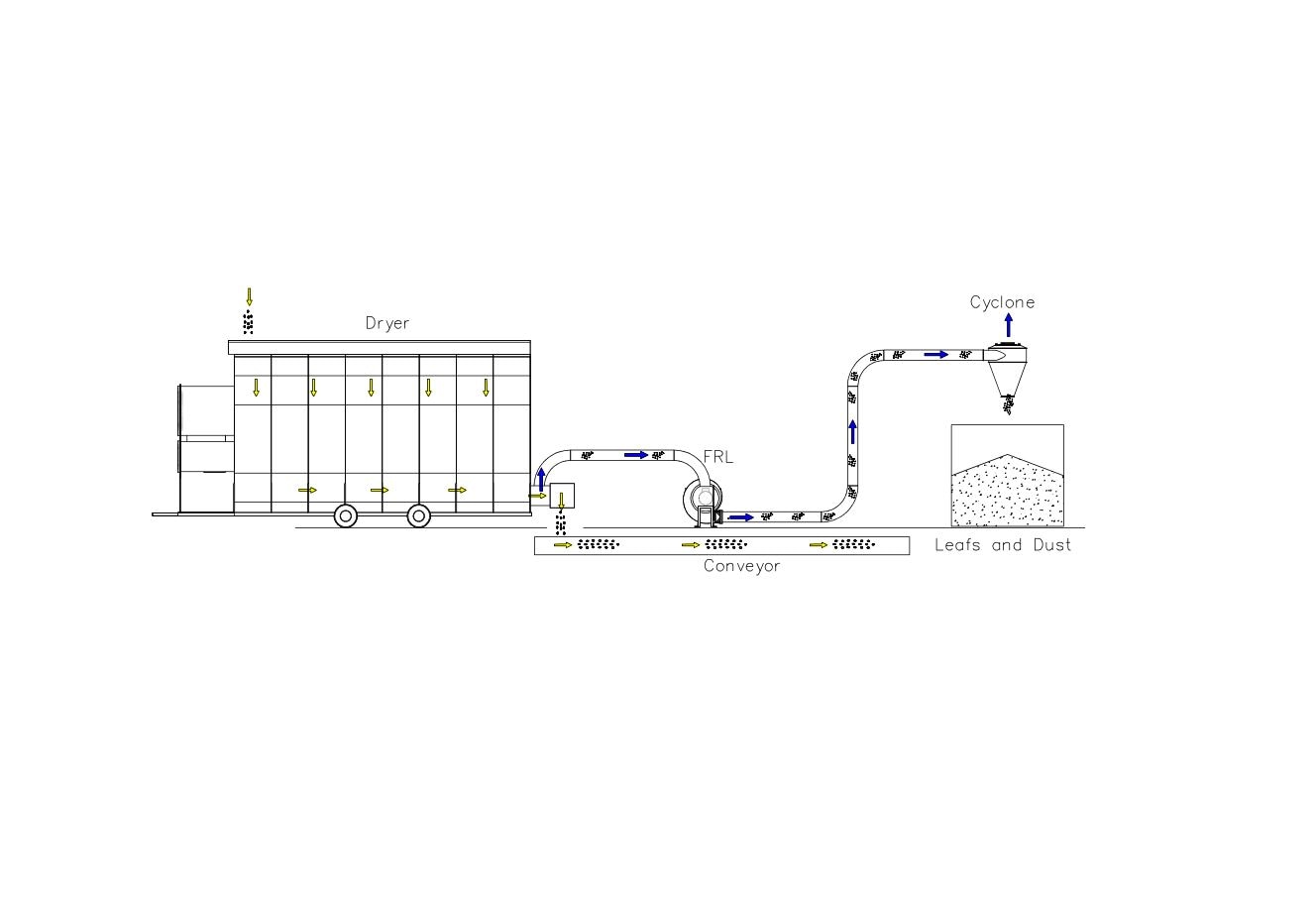
Cyclone Aspiration and Grain Cleaning at Dryer Discharge
During drying, especially in crops like corn, light material such as bees’ wings and dust tend to cling to wet kernels. Once the crop passes through the dryer, this debris is loosened and can be efficiently removed using a cyclone aspiration system or an aspirator grain cleaner.
This aspiration cleaning method uses vacuum technology to extract unwanted materials at the discharge point, ensuring cleaner grain before it enters storage. By targeting the light particles right after drying, this system enhances grain cleaning performance and reduces the buildup of contaminants—especially at the center of the silo under the filling point—where poor ventilation can otherwise increase spoilage risks.
Whether you’re managing corn cleaning or general grain handling, aspiration cleaning ensures better airflow during storage and minimizes the risk of spoilage due to dust and leaf accumulation.
Download Resources
Download the latest Kongskilde PDF documents, brochures, data sheets, manuals, and more.